Kafka 最初由 Linkedin 公司开发,是一个分布式、分区的、多副本的、多订阅者,基于 zookeeper 协调的分布式日志系统(也可以当做 MQ 系统)。常见可以用于 web/nginx 日志、访问日志,消息服务等等,Linkedin 于 2010 年贡献给了 Apache 基金会并成为顶级开源项目。
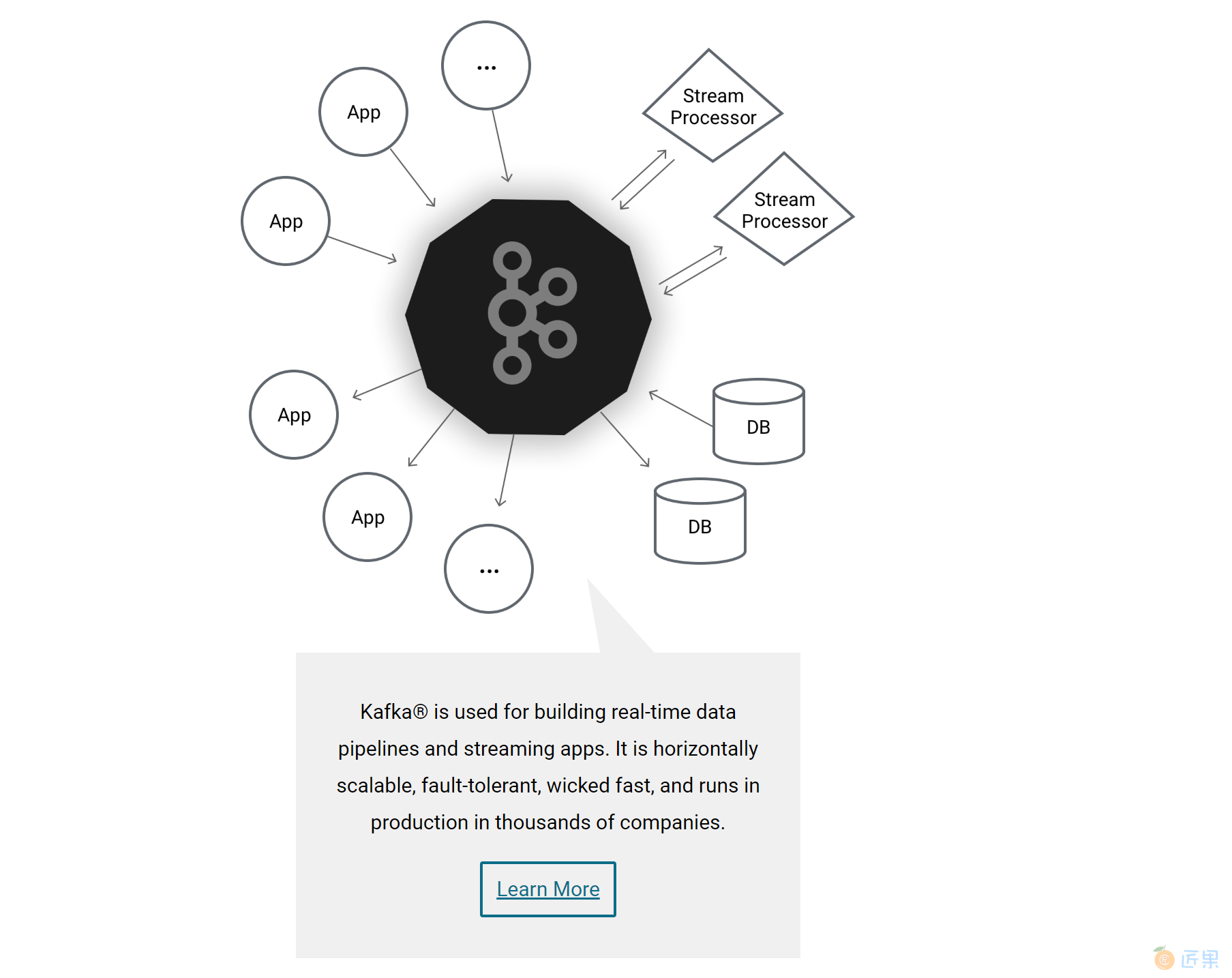
Kafka® 用于构建实时数据管道和流应用程序。它具有横向可扩展性、容错性、极快的速度,并在数千家公司的生产中运行。
主要应用场景是:日志收集系统和消息系统。Kafka 的主要设计目标:
- 以时间复杂度为 O(1) 的方式提供消息持久化能力,即使对 TB 级以上数据也能保证常数时间的访问性能。
- 高吞吐率。即使在非常廉价的商用机器上也能做到单机支持每秒 10 万+条消息的传输。
- 支持 Kafka Server 间的消息分区,及分布式消费,同时保证每个分区内的消息顺序传输。
- 同时支持离线数据处理和实时数据处理。
- 支持在线水平扩展。
9.5.1 概念
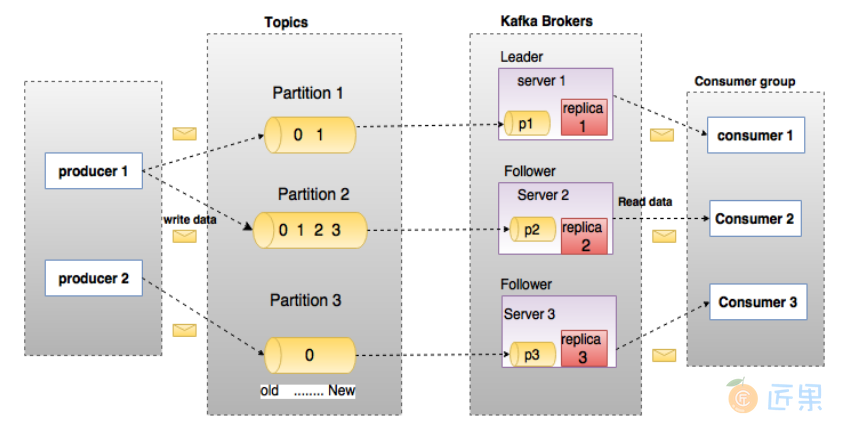
为了理解 Kafka,需要了解 Kafka 中的术语。下图展示了 Kafka 的相关概念以及之间的关系:
上图中一个 topic 配置了 3 个 partition。Partition1 有两个 offset:0和1。Partition2 有4个 offset。Partition3 有1个 offset。
如果一个 topic 的副本数为 3,那么 Kafka 将在集群中为每个 partition 创建 3 个相同的副本。集群中的每个 broker 存储一个或多个 partition。多个 producer 和 consumer 可同时生产和消费数据。
9.5.1.1 broker
Kafka 集群包含一个或多个服务器,服务器节点称为 broker。broker 存储 topic 的数据。如果某 topic 有 N 个 partition,集群有 N 个 broker,那么每个 broker 存储该 topic 的一个 partition。
如果某 topic 有 N 个 partition,集群有(N+M)个 broker,那么其中有N个 broker存储该 topic的一个 partition,剩下的M个 broker 不存储该 topic 的 partition 数据。
如果某 topic 有N个 partition,集群中 broker 数目少于N个,那么一个 broker 存储该 topic 的一个或多个 partition。在实际生产环境中,尽量避免这种情况的发生,这种情况容易导致 Kafka 集群数据不均衡。
9.5.1.2 Topic
每条发布到 Kafka 集群的消息都有一个类别,这个类别被称为 Topic。(物理上不同 Topic 的消息分开存储,逻辑上一个 Topic 的消息虽然保存于一个或多个 broker 上但用户只需指定消息的 Topic 即可生产或消费数据而不必关心数据存于何处)。
Topic 类似于数据库的表名。
9.5.1.3 Partition
topic 中的数据分割为一个或多个 partition。每个 topic 至少有一个 partition。每个 partition 中的数据使用多个 segment 文件存储。partition 中的数据是有序的,不同 partition 间的数据丢失了数据的顺序。如果 topic 有多个 partition,消费数据时就不能保证数据的顺序。在需要严格保证消息的消费顺序的场景下,需要将 partition 数目设为1。
9.5.1.4 Producer
生产者即数据的发布者,该角色将消息发布到 Kafka 的 topic 中。broker 接收到生产者发送的消息后,broker 将该消息追加到当前用于追加数据的 segment 文件中。生产者发送的消息,存储到一个 partition 中,生产者也可以指定数据存储的 partition。
9.5.1.5 Consumer
消费者就是数据的使用者,可以从 broker 中读取数据。消费者可以消费多个 topic 中的数据。
9.5.1.6 Consumer Group
每个 Consumer 属于一个特定的 Consumer Group(可为每个 Consumer 指定 group name,若不指定 group name 则属于默认的 group)。
9.5.1.7 Leader
每个 partition 有多个副本,其中有且仅有一个作为 Leader,Leade r是当前负责数据的读写的 partition。
9.5.1.8 Follower
Follower 跟随 Leader,所有写请求都通过 Leader 路由,数据变更会广播给所有 Follower,Follower 与 Leader 保持数据同步。如果 Leader 失效,则从 Follower 中选举出一个新的 Leader。当 Follower 与 Leader 挂掉、卡住或者同步太慢,leader 会把这个 follower 从“in sync replicas”(ISR)列表中删除,重新创建一个 Follower。
9.5.2 安装配置
到 官网下载 最新版本的使用Scala 2.12的 Kafka 2.3.1,Kafka 需要依赖 ZooKeeper,需要到 zookeeper 官网下载 最新版本的 ZooKeeper 3.5.6 并提前安装配置好。
Kafka uses ZooKeeper so you need to first start a ZooKeeper server if you don't already have one. You can use the convenience script packaged with kafka to get a quick-and-dirty single-node ZooKeeper instance.
bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties
9.5.2.1 安装 ZooKeeper
解压下载后的 apache-zookeeper-3.5.6-bin.tar.gz 到磁盘,例如C:\Java\apache-zookeeper-3.5.6-bin目录。
Windows 下使用 WinRAR 解压 apache-zookeeper-3.5.6-bin.tar.gz 有可能会出现错误,可使用7zip解压即可。
在 ZooKeeper 安装目录下创建 data 目录,例如C:\Java\apache-zookeeper-3.5.6-bin\data。
进入C:\Java\apache-zookeeper-3.5.6-bin\conf目录,拷贝 zoo_sample.cfg 为 zoo.cfg,然后编辑配置信息。
# The number of milliseconds of each tick
tickTime=2000
# The number of ticks that the initial
# synchronization phase can take
initLimit=10
# The number of ticks that can pass between
# sending a request and getting an acknowledgement
syncLimit=5
# the directory where the snapshot is stored.
# do not use /tmp for storage, /tmp here is just
# example sakes.
dataDir=C:/Java/apache-zookeeper-3.5.6-bin/data
# the port at which the clients will connect
clientPort=2181
# the maximum number of client connections.
# increase this if you need to handle more clients
#maxClientCnxns=60
#
# Be sure to read the maintenance section of the
# administrator guide before turning on autopurge.
#
# http://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/current/zookeeperAdmin.html#sc_maintenance
#
# The number of snapshots to retain in dataDir
#autopurge.snapRetainCount=3
# Purge task interval in hours
# Set to "0" to disable auto purge feature
#autopurge.purgeInterval=1
打开命令提示符窗口,进入 ZooKeeper 的 bin 目录,执行zkServer.cmd命令启动服务。
在学习环境下,我们就不演示配置 ZooKeeper 高可用集群了。
9.5.2.2 安装 Kafka
解压下载后的 kafka_2.12-2.3.1.tgz 文件到磁盘,例如C:\Java\kafka_2.12-2.3.1目录。
在 Kafka 安装目录下创建 logs 目录(C:\Java\kafka_2.12-2.3.1\logs),用来存放日志文件。
编辑 Kafka 安装目录下 config 目录下的 server.properties 文件(C:\Java\kafka_2.12-2.3.1\config\server.properties)。修改的地方为log.dirs=C:/Java/kafka_2.12-2.3.1/logs(第60行)。需要检查连接到 ZooKeeper 的配置信息zookeeper.connect=localhost:2181(第123行)是否正确。
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# see kafka.server.KafkaConfig for additional details and defaults
############################# Server Basics #############################
# The id of the broker. This must be set to a unique integer for each broker.
broker.id=0
############################# Socket Server Settings #############################
# The address the socket server listens on. It will get the value returned from
# java.net.InetAddress.getCanonicalHostName() if not configured.
# FORMAT:
# listeners = listener_name://host_name:port
# EXAMPLE:
# listeners = PLAINTEXT://your.host.name:9092
#listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
# Hostname and port the broker will advertise to producers and consumers. If not set,
# it uses the value for "listeners" if configured. Otherwise, it will use the value
# returned from java.net.InetAddress.getCanonicalHostName().
#advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://your.host.name:9092
# Maps listener names to security protocols, the default is for them to be the same. See the config documentation for more details
#listener.security.protocol.map=PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT,SSL:SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT:SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL:SASL_SSL
# The number of threads that the server uses for receiving requests from the network and sending responses to the network
num.network.threads=3
# The number of threads that the server uses for processing requests, which may include disk I/O
num.io.threads=8
# The send buffer (SO_SNDBUF) used by the socket server
socket.send.buffer.bytes=102400
# The receive buffer (SO_RCVBUF) used by the socket server
socket.receive.buffer.bytes=102400
# The maximum size of a request that the socket server will accept (protection against OOM)
socket.request.max.bytes=104857600
############################# Log Basics #############################
# A comma separated list of directories under which to store log files
log.dirs=C:/Java/kafka_2.12-2.3.1/logs
# The default number of log partitions per topic. More partitions allow greater
# parallelism for consumption, but this will also result in more files across
# the brokers.
num.partitions=1
# The number of threads per data directory to be used for log recovery at startup and flushing at shutdown.
# This value is recommended to be increased for installations with data dirs located in RAID array.
num.recovery.threads.per.data.dir=1
############################# Internal Topic Settings #############################
# The replication factor for the group metadata internal topics "__consumer_offsets" and "__transaction_state"
# For anything other than development testing, a value greater than 1 is recommended for to ensure availability such as 3.
offsets.topic.replication.factor=1
transaction.state.log.replication.factor=1
transaction.state.log.min.isr=1
############################# Log Flush Policy #############################
# Messages are immediately written to the filesystem but by default we only fsync() to sync
# the OS cache lazily. The following configurations control the flush of data to disk.
# There are a few important trade-offs here:
# 1. Durability: Unflushed data may be lost if you are not using replication.
# 2. Latency: Very large flush intervals may lead to latency spikes when the flush does occur as there will be a lot of data to flush.
# 3. Throughput: The flush is generally the most expensive operation, and a small flush interval may lead to excessive seeks.
# The settings below allow one to configure the flush policy to flush data after a period of time or
# every N messages (or both). This can be done globally and overridden on a per-topic basis.
# The number of messages to accept before forcing a flush of data to disk
#log.flush.interval.messages=10000
# The maximum amount of time a message can sit in a log before we force a flush
#log.flush.interval.ms=1000
############################# Log Retention Policy #############################
# The following configurations control the disposal of log segments. The policy can
# be set to delete segments after a period of time, or after a given size has accumulated.
# A segment will be deleted whenever *either* of these criteria are met. Deletion always happens
# from the end of the log.
# The minimum age of a log file to be eligible for deletion due to age
log.retention.hours=168
# A size-based retention policy for logs. Segments are pruned from the log unless the remaining
# segments drop below log.retention.bytes. Functions independently of log.retention.hours.
#log.retention.bytes=1073741824
# The maximum size of a log segment file. When this size is reached a new log segment will be created.
log.segment.bytes=1073741824
# The interval at which log segments are checked to see if they can be deleted according
# to the retention policies
log.retention.check.interval.ms=300000
############################# Zookeeper #############################
# Zookeeper connection string (see zookeeper docs for details).
# This is a comma separated host:port pairs, each corresponding to a zk
# server. e.g. "127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002".
# You can also append an optional chroot string to the urls to specify the
# root directory for all kafka znodes.
zookeeper.connect=localhost:2181
# Timeout in ms for connecting to zookeeper
zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms=6000
############################# Group Coordinator Settings #############################
# The following configuration specifies the time, in milliseconds, that the GroupCoordinator will delay the initial consumer rebalance.
# The rebalance will be further delayed by the value of group.initial.rebalance.delay.ms as new members join the group, up to a maximum of max.poll.interval.ms.
# The default value for this is 3 seconds.
# We override this to 0 here as it makes for a better out-of-the-box experience for development and testing.
# However, in production environments the default value of 3 seconds is more suitable as this will help to avoid unnecessary, and potentially expensive, rebalances during application startup.
group.initial.rebalance.delay.ms=0
打开命令提示符窗口,进入C:\Java\kafka_2.12-2.3.1\bin\windows目录,执行kafka-server-start.bat ..\..\config\server.properties命令,启动 Kafka 服务器,默认服务监听端口 9092。
[2019-12-08 11:21:44,907] INFO Awaiting socket connections on 0.0.0.0:9092. (kafka.network.Acceptor)
9.5.3 与 Spring Boot 集成
Spring 为 Kafka 提供了依赖配置,集成非常方便。并且提供 KafkaTemplate 模板类来简化编码过程。
创建新的 Spring Boot 项目,添加Spring Web和Spring for Apache Kafka依赖。
pom 文件中关键的 Kafka 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
在 application.yml 配置文件中配置连接到 Kafka 的信息:
server:
port: 9090
spring:
kafka:
bootstrap-servers:
- 127.0.0.1:9092
consumer:
group-id: test-consumer-group
key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
value-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
producer:
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
value-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
创建消息生产者 KafkaProducer 类,添加回调方法(消息消费成功后消息中间件会回调消息生产者):
package com.example.kafka.producer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.SendResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureCallback;
@Component
public class KafkaProducer {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
public void sendMessage(String msg) {
ListenableFuture<SendResult<String, String>> future = kafkaTemplate.send("KafkaTopic", msg);
future.addCallback(new ListenableFutureCallback<SendResult<String, String>>() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("Send Message Failure:" + throwable.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult<String, String> sendResult) {
System.out.println("Send Message Success:" + sendResult.toString());
}
});
}
}
创建消息消费者 KafkaConsumer 类:
package com.example.kafka.consumer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class KafkaConsumer {
@KafkaListener(topics = {"KafkaTopic"})
public void listen(ConsumerRecord<?, ?> record) {
System.out.println("RocketMQ Consumer consume message: " + record.value());
}
}
创建控制器 KafkaController 类与用户交互:
package com.example.kafka.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.kafka.producer.KafkaProducer;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/kafka/")
public class KafkaController {
@Autowired
KafkaProducer kafkaProducer;
@RequestMapping("/send")
public String sendMsg(String msg) {
kafkaProducer.sendMessage(msg);
return msg + " Sended to KafkaTopic.";
}
}
这个时候启动 Spring Boot 应用可能会报错,原因是没有创建“KafkaTopic”主题,需要提前在 Kafka 中创建这个“KafkaTopic”主题。
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Failed to start bean 'org.springframework.kafka.config.internalKafkaListenerEndpointRegistry'; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: Topic(s) [KafkaTopic] is/are not present and missingTopicsFatal is true
创建KafkaTopic主题:
kafka-topics.bat -create --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 -replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic KafkaTopic查看主题:
kafka-topics -list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
在确保 Kafka 消息中间件中有“KafkaTopic”主题的前提下启动 Spring Boot 应用。
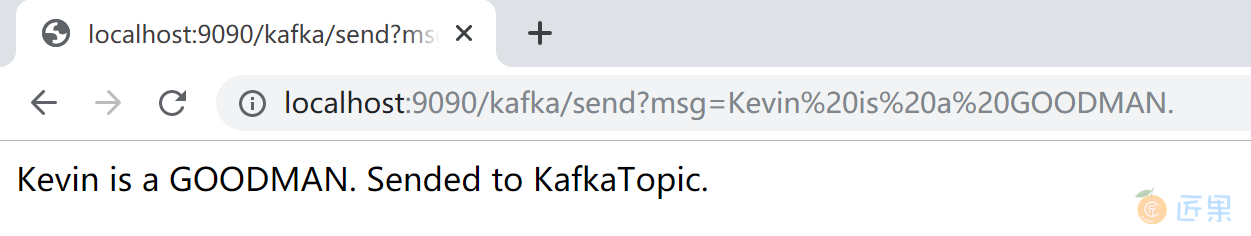
打开浏览器,访问 http://localhost:9090/kafka/send?msg=Kevin is a GOODMAN. is a GOODMAN.) 地址,向 Kafka 发送消息。
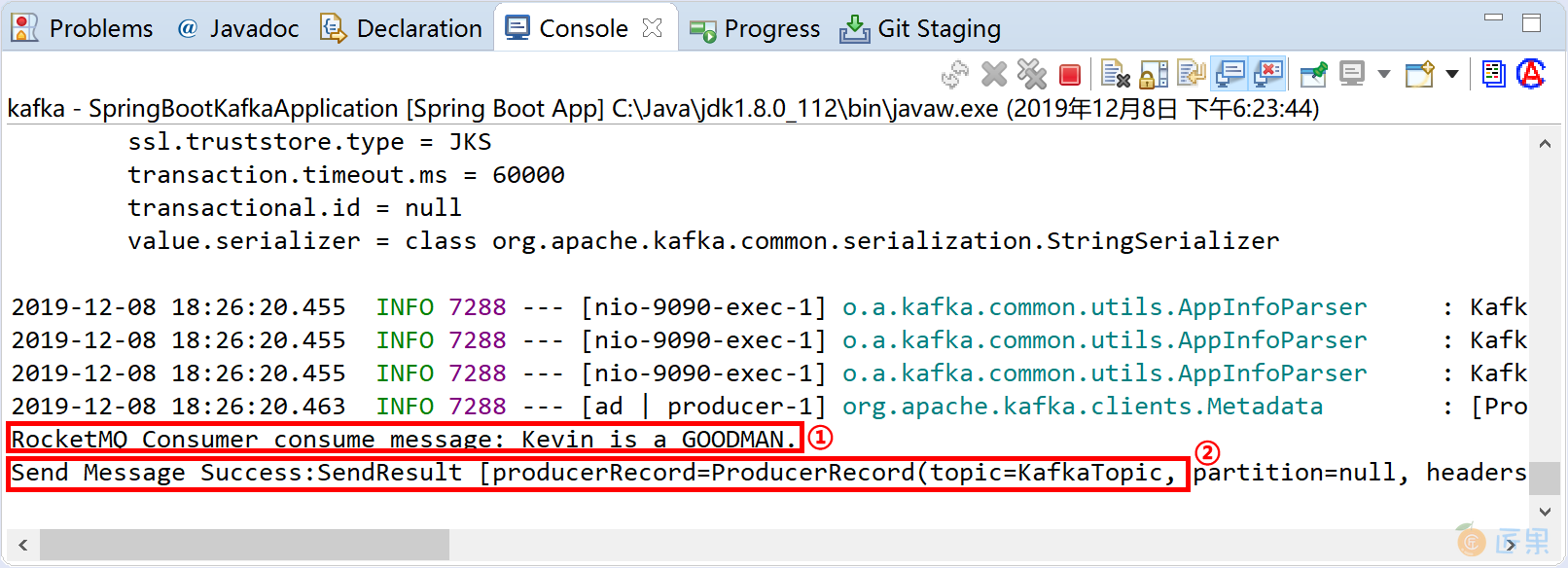
观察 Spring Boot 应用的控制台,消息消费者 KafkaConsumer 消费消息后在控制台上输出正确的消息RocketMQ Consumer consume message: Kevin is a GOODMAN.,还可以看到回调消息生产者输出的结果Send Message Success...。